Parallelization Workflow - Stop over-engineering your AI automation: Episode 3
AI Agents are the talk of the town, and rightly so. They are incredible for unpredictable tasks. But for 80% of business automation, you're overcomplicating it. A simple, efficient LLM workflow is often the faster, cheaper, and more reliable answer.
There are times, and most of the times, where a simple automated workflow can do the trick in much lesser of cost & complexity. This series is intended to help you understand if your task fits any of the workflow template, rather than an AI agent.
Define your problem
In case you think that your task can be broken down into multiple subtasks, that can be resolved in parallel, offering you speed or in case you want to use multiple agents to work on the same issue from multiple views, to encompass wider range of points to be included in your task, you can use Parallelization Workflow.
When to use Parallelization
There are usecases where our LLMs have to work in parallel and then have their outputs aggregated programmatically, that's where this workflow is used. This workflow can manifest itself in 2 variations:
- Sectioning: Breaking a task into independent subtasks that can run in parallel
- - Voting: Running the same task multiple times to get diverse outputs and then aggregating the same to create one single output.
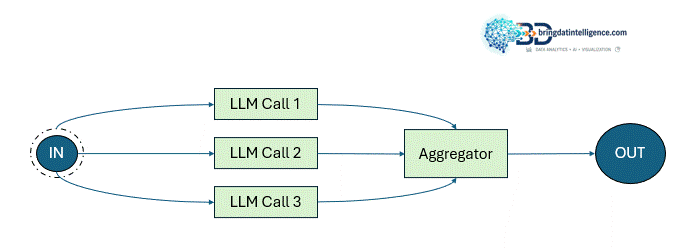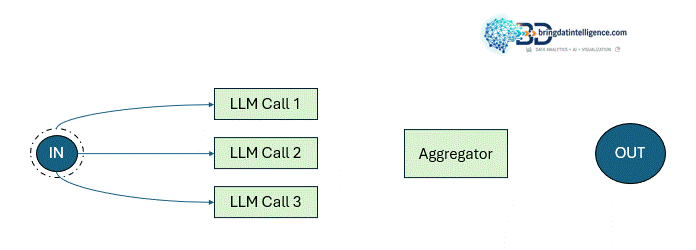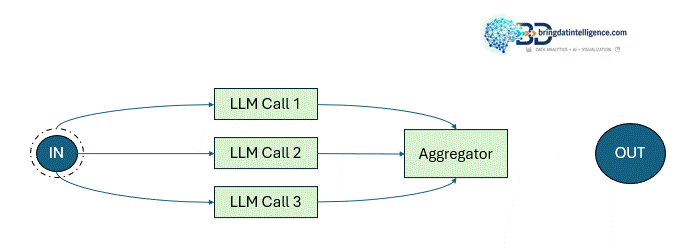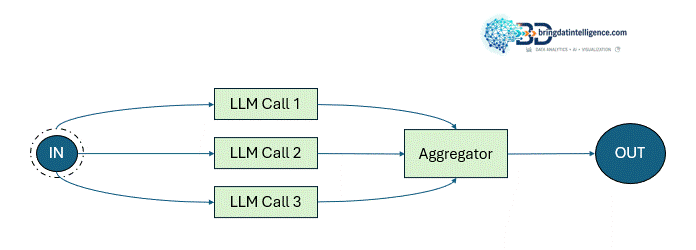
When to use Parallelization
This kind of workflow is best suited in scenarios like:
- One instance resolves user query, while the other ensures that it adheres to the established governance guardrails
- Evaluating LLM output on different parameters of evaluation
- Reviewing code for vulnerabilities
Some use cases
- High volume document processing
- Market research covering various angles
- Code testing
- Multi Modal Content Analysis
